- Before we try to understand the Humidity sensor we need to understand what is humidity,
The amount of water vapor present in the air is known as humidity. The humidity will be high if there is a lot of water vapor in the atmosphere. It feels wetter outside as the humidity rises. - An electronic device known as a humidity sensor monitors the humidity in its surroundings and then transforms the data into an appropriate electrical signal. Technically called HYGROMETER.
- Now, humidity is measured in two ways as Relative Humidity and Absolute Humidity.
And there are different sensors to measure both types of humidity. They can be classified as Relative humidity sensors and Absolute humidity sensors.
Relative Humidity Sensor
- Relative humidity is calculated by comparing the live humidity reading at a given temperature to the maximum amount of humidity for air at the same temperature. RH sensors must therefore measure temperature to determine relative humidity.
- There are again two types of sensors to calculate relative humidity, Capacitive, and Resistive humidity sensors. We will understand the working of both the sensors one by one.
Capacitive Humidity Sensor
- Capacitive Humidity Sensors, which are simply based on capacitive effect, are one of the most basic types of Humidity Sensors available.
Working of Capacitive Humidity Sensor
- A capacitive humidity sensor measures relative humidity by placing a thin strip of metal oxide between two electrodes. The capacitance of the metal increases or decreases at a rate that is proportional to the change in humidity in the sensor’s environment. The difference in charge (voltage) caused by humidity increases is amplified and sent to the embedded computer for processing.
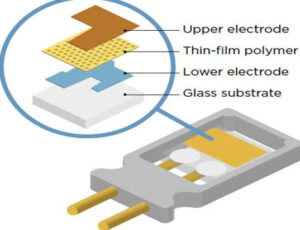
- As the sensor uses water vapor in the air, placing the sensor in the path of moving air allows it to respond faster.
- A capacitive humidity sensor is used to measure relative humidity with a usual range of 5 to 95 % rectum.
Resistive Humidity Sensor
- Another type of Humidity Sensor is the resistive humidity sensor, which measures resistance (impedance) or electrical conductivity. The principle underlying resistive humidity sensors is that the conductivity of non-metallic conductors varies with their water content.
Working of Resistive Humidity Sensor
- Resistive humidity sensors use ions in salts to measure the electrical impedance of atoms. The resistance of the electrodes on either side of the salt medium changes as humidity changes, based on the humidity of the surrounding air.
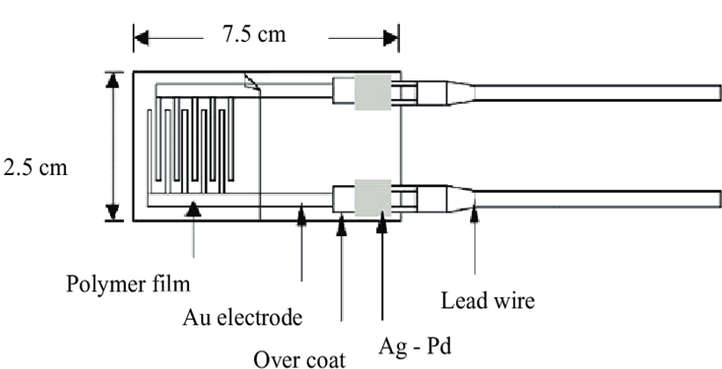
- The Resistive Humidity Sensor is typically made of materials with low resistivity, and this resistivity varies significantly with humidity. Resistance and humidity have an inverse exponential relationship. On top of two electrodes, the low resistivity material is deposited.
Absolute Humidity Sensor
- Absolute humidity is a measure of the actual amount of water vapor (moisture) in the air (grams per cubic meter), regardless of the air’s temperature.
- Because they measure Absolute Humidity, Thermal Humidity Sensors are also known as Absolute Humidity (AH) Sensors. They assess the thermal conductivity of both dry air and air containing water vapor. Absolute humidity is related to the difference in individual thermal conductivities.
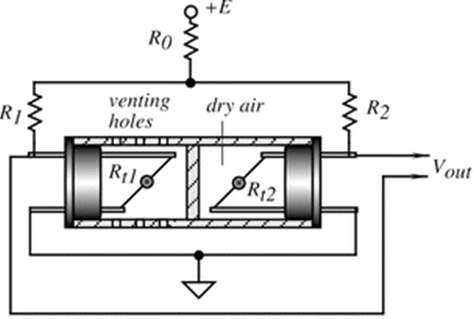
- They are ideal for places with high temperatures or corrosive environments.
- Two thermal sensors conduct electricity, one thermal sensor measures the ambient air, while the other is encased in dry nitrogen to measure the humidity of the environment with this humidity sensor.

- The difference between the two collected data then allows you to calculate the humidity. In other words, they determine absolute humidity by calculating the difference in thermal conductivity between dry and humid air.
Applications of Humidity Sensor
- Moisture analyzers include humidity sensors and allow for the measurement and control of humidity and moisture conditions in manufacturing facilities as part of process control applications.
- The humidity sensors are installed inside the AC and measure the moisture and temperature of the air. Controlling can help save those who have difficulty breathing by keeping the moisture in the air at the desired level.
- Humidity control is required for medical equipment such as sterilizers, incubators, ventilators, and so on. The humidity sensor is also used in biological and pharmaceutical processes.
- Semiconductor fabrication plants must maintain extremely accurate humidity and temperature values, as even a minute difference can have a significant impact on production.
- Humidity sensors in HVAC systems are critical for maintaining proper climate conditions while conserving energy.
