The TRF, tuned radio frequency radio receiver was widely used in the early days of radio, but is hardly used today
- This receiver was popular in the 1920s and a TRF is a type of radio receiver that is controlled by one or more RF amplifier stages followed by a detector circuit to extract the audio signal and usually an audio frequency amplifier.
- Early models could be uninteresting to operate because when tuning in a station each stage had to be individually adjusted to the station’s frequency.
- But now latest models had ganged tuning, the tuning mechanisms of all stages being linked together, and operated by just one control knob.
- In the 1930’s it was replaced by the superheterodyne receiver patented by Edwin Armstrong.
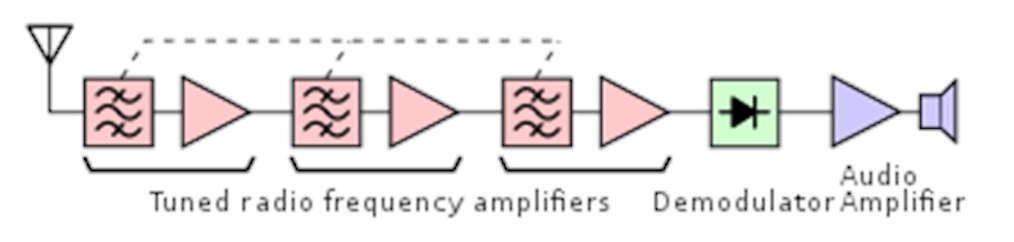
- It consisted of three section RF amplifier, demodulator, and audio amplifier.
- The signal received from the antenna is weak and noisy so this signal is given to a broadband RF amplifier.
- This RF amplifier enhances the signal-to-noise ratio and amplifies the signal. Then this signal passed through AM detector or demodulator.
- The output of AM detector or demodulator is an audio signal. The detected audio signal is then amplified by the audio power amplifier.
- The audio amplifier output give to the speaker and then it finally produces the sound.
- The RF amplifier is tuned to a specific frequency that is to be received. Hence if another frequency is to receive, then another TRF receiver should be used.
- By using the RF amplifier tuned to a wide range of frequencies this problem is solved. But this reduces the selectivity of the receiver.
Advantages of TRF Receiver
- Simplest type of receiver since it does not involve mixing and IF operation.
- Very much suitable to receive single frequency.
- TRF receivers have good sensitivity.
Disadvantages of TRF Receiver
- Bandwidth changes with center frequency, when the TRF receiver is used to receive a wide range of frequencies.
- Multiple stages of RF amplifiers are used. This can lead to instability since they all are tuned to the same center frequency. Hence stagger tuning is to be used.
- The gain of the TRF receiver is not uniform over a wide range of frequencies.
Application of TRF Receiver
- It was used in the early days of wire-less technology but it is rarely used today as other techniques offering much better performance are available.
Limitations of TRF Receiver
- It suffers from variations in BW over the tuning range ( s 40 – 1650 kHz).
- The gain of TRF RX is not uniform over the tuning range.
- The TRF is unstable at high frequency.
- Gang tuning of more capacitors simultaneously is difficult.
