- The NTE159M is a general-purpose PNP transistor with a maximum gain of 300 and a collector current of 600mA. It has a low collector saturation voltage of 1V and can be used in switching and amplifier circuits.

Now we know that NTE159M is nothing but a simple three-terminal PNP resistor, lets try to understand, what is a PNP resistor and how does it work?
- A PNP transistor is a bipolar junction transistor composed of an N-type semiconductor sandwiched between two P-type semiconductors. A PNP transistor has three terminals: a Collector (C), an Emitter (E), and a Base (B) (B). The PNP transistor functions similarly to two PN junction diodes connected back to back.
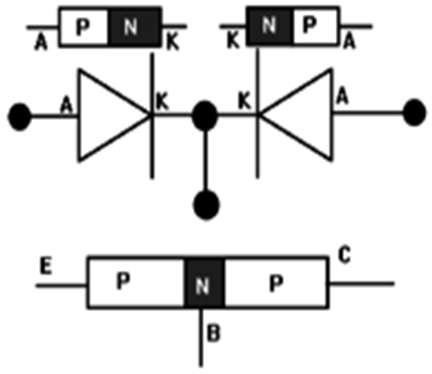
- A voltage source (VEB positive )’s terminal is connected to the Emitter (P-type), and the negative terminal is connected to the Base terminal (N-type). As a result, the Emitter-Base junction is biased forward.
![]()
- And the positive terminal of a voltage source (VCB) is linked to the Base terminal (N-type), while the negative terminal is linked to the Collector terminal (P-type). As a result, the Collector-Base junction is biased in reverse.
- Now the emitter-base junction is forward biased, the emitter pushes the holes towards the base region, resulting in an emitter current. Electrons combine with holes as they move into the N-type semiconductor or base.
- The base has a light doping and is relatively thin. As a result, only a few holes combine with the electrons, with the remainder moving towards the collector space charge layer. The base current is produced by this phenomenon. In p-n-p transistors, the current is carried by holes.
Pin Configurations NTE159M Transistor
- It has three terminals Base, Collector, and Emitter as shown below
![]()
- Base – Controls the biasing of the transistor; used to turn the transistor on or off.
- Collector – This pin allows current to flow and is normally connected to a load.
- Emitter – This pin is normally connected to a load and allows current to flow.
Features and specifications of NTE159M Transistor
- To-18 Package is available.
- The collector-base voltage (VCB) is set to 60V.
- The emitter-base voltage (VBE) is 5 volts.
- The constant collector current (IC) is 600mA.
- The frequency of transition is 200 MHz.
- 100 to 300 DC Current Gain (hFE).
- Power dissipation is 0.4 W.
Applications of NTE159M Transistor
- NTE159M are used as switches.
- These are employed in amplifying circuits.
- In matched pair circuits, PNP transistors are used to generate continuous power there also NTE159M can be employed.
- Darlington pair circuits also use this transistor.
- Class B amplifier designs.
