- Single transistor amplifiers typically don’t have enough gain or output impedance matching for most systems. The only way to solve the problem is to mix various amplification stages. We’re going to demonstrate a straightforward two-transistor amplifier in this amplifier circuit. One transistor, one resistor, and one capacitor were used to create a very straightforward amplifier in the single transistor amplifier circuit, although an amplifier with two transistors was designed.
- The two transistor amplifier has a low output while offering a fair amount of resistance. It is the perfect amplifier circuit for uses when more output power than the single transistor stage is needed.
Two-Transistor Audio Amplifier Circuit
- To build our amplifier circuit, we’ll utilize two stages and two distinct transistors, NPN and PNP. Common names for this circuit include two transistor amplifiers and two-stage amplifiers. The circuit offers more bandwidth at a more affordable price.
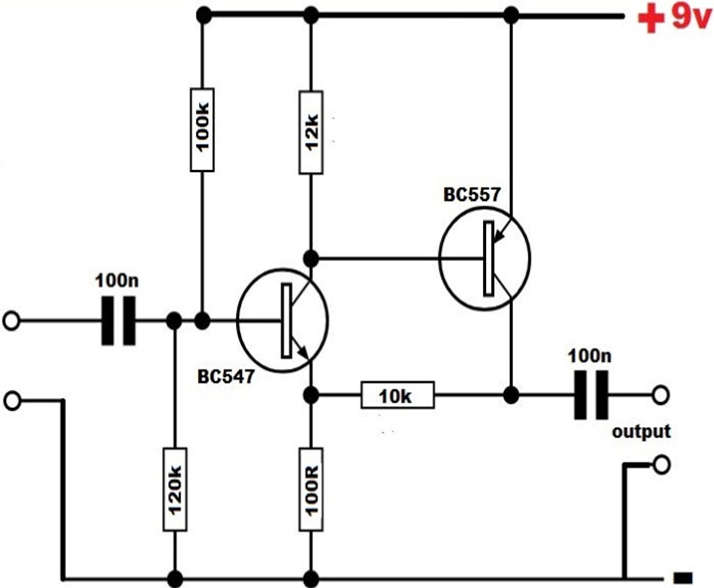
Working of Two Transistor Amplifier
- Two stages make up these two transistor amplifier circuits. The NPN transistor is utilized in the first stage. Current flows between the collector and emitter of the first transistor (NPN) when the circuit is powered and an audio signal is applied at the transistor’s base. The flowing current is therefore inversely correlated with the auditory signal. The signal is increased by the transistor, which then outputs it to the collector. This transistor activates the second transistor because its collector is coupled to the PNP transistor’s base. To establish the base of each transistor, 100K and 12K resistors are present. The PNP transistor’s collector is where the output of the amplifier with high bandwidth and high gain may be seen.
Advantages of Two Transistor Amplifier
- Increase in Gain.
- Depending on how similar or unlike each stage’s bandwidth is, the bandwidth change.
Disadvantages of Two Transistor Amplifier
- The Q point and subsequent distortion may be impacted by the loading of one stage onto the preceding stage.
- The kind of coupling that will influence the coupling methods’ gain at a specific frequency.
Application of Transistor as an Amplifier
- For radio signals.
- Portable devices.
- Electronics audio devices.
- Transistor as an amplifier is used in optical fiber communication.
- Since the intensity of the output signal is high, it finds application in long-distance communication.
- The amplification of radio signals is possible because of such amplifiers.
- Amplifiers are used in wireless communication.
- The audio amplification is possible because of the use of amplifiers.
