![]()
Single layer PCB
- Single layer printed circuit board is also known as the single-sided printed circuit board. Single-layer PCB is the simplest low-cost PCB as compared to other PCBs. This type of PCB has only one single layer of base substrate fiberglass and only one single conductive copper layer hole for electronic components is on one side. Since there is only a conductive layer forming the circuit it is called a single-sided printed circuit board or one layer printed circuit board or single-layer printed circuit board. Single-layer PCB is Ideal for simple low-density designs as it has a lower cost as compared to other PCBs, especially for high volume orders. It is the most common popular PCBs. Single-layer printed circuited board is commonly used in radio equipment, calculator, LED panel, digital camera, radio and stereo equipment, etc.
![]()
Double-layer PCB
- This type of PCB has one single layer of the base substrate but a conductive copper layer on both sides of the substrate. The solar mask is applied on both sides of the board holes for the electronic components have to be plated for conductivity on both the circuits. Electronic components are soldered on both sides. SMD I.e surface mount device can be soldered on either side of this type of PCB. SMD components can be soldered with surface mount technology. Since there are two or double conductive layers forming the circuit it is called double side PCB or two-layer PCB. Double layer PCBs use for more complex circuitry as there is more space. Double layer PCBs are commonly used in consumer electronics, lighting systems, vending machines, amplifiers, automotive dashboards, etc
![]()
Multilayer PCB
- Multilayer PCB is a PCB with more than two layers. These types of PCB must have a minimum of three conductive layers of conductive material or copper layer. All the layers can be interconnected with copper-plated holes. This layer can be 4,6 up to 40 layer all the active & passive electronic components assembled on top & bottom layers. SMD I.e surface mount device can be soldered on either side of this type of PCB. SMD components can be soldered with surface mount technology. These boards are secured together with a specialized glue and sandwiched between pieces of insulation to ensure that excess heat doesn’t melt any of the components. The largest multi-layer PCB ever built was 50 layers thick with many layers of PCB which are suitable for a broad range of complicated electrical tasks application wherewith multi layer PCBs would be beneficial for data storage GPS technology, satellite system, whether analysis, medical equipment, etc.
![]()
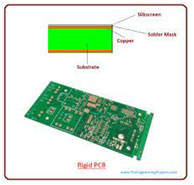
Rigid PCB
- These PCBs are made out of a solid substrate material that prevents the board from twisting. Possibly the most common example of a rigid PCB is a computer motherboard. The motherboard is a multi-layer PCB designed to allocate electricity from the supply while simultaneously allowing communication between all of the many parts of the computer such as CPU, GPU, and RAM. Rigid Circuit Board is made of a solid substrate with copper tracks and component layouts. This PCB itself to be set up in one shape and remaining that shape only. Rigid PCBs can be anything from single-layer PCB to up to 8 or 10 multi-layer PCBs.The advantage of using rigid PCB is it generates low electronic noise and minimizes cross-talk.
 Flexible PCB
Flexible PCB
- Flexible PCBs are printed circuit boards that are designed to be flexible and malleable. Flexible PCBs are made of materials that can flex and move such as plastic. Flexible PCBs come in single, double, or multi-layer formats as they need to print on a flexible material that’s why it tends to more fabrication cost. Still, Flexible PCBs have many advantages like is more reliable and long-lasting, less size, and low weight. Flexible PCB is used in a wide range of applications including Flex solar cells, automotive industries, LEDs, etc.
![]()
Flex -rigid PCB
- A combination of flexible PCB and rigid PCB is called a Flex-rigid PCB. It consists of both rigid and flexible substrates that are laminated together to form a single circuit board. This type of PCB exhibits the benefits of both rigid wells as flexible circuit boards. It allows for a more streamlined design reducing the overall board size. They are most often found applications are used in military, aerospace, and medical devices.
![]()
