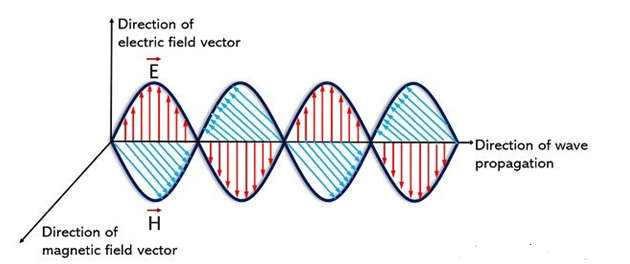
- Polarization is defined as the special property of electromagnetic waves that provides a specific relation between the time-varying direction and magnitude of the vibrating electric field.
- Polarization of an antenna is loosely defined as the direction of the electromagnetic fields produced by the antenna as energy radiates away from it.
- These directional fields determine the direction in which the energy moves away from or is received by an antenna.
Types of Polarization
- Linear Polarization
- Circular Polarization
- Elliptical Polarization
1. Linear Polarization
- A type of polarization in which all the waves possess similar alignment in space either vertical or horizontal is known as linear polarization.
a) Vertical polarization-
- It is the linear polarization in which the wave travels perpendicular to the surface of the Earth.
b)Horizontal Polarization-
- The linear polarization in which the wave travels horizontally to the surface of the earth.
c) Slant Polarization-
- In a slant polarization antenna, rather than horizontal and vertical, the polarization is at –45 degrees and +45 degrees from a reference plane of 0 degrees(surface of the earth).
2. Circular Polarization
- Circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
- It occurs when the two orthogonal electric field component vectors are of equal magnitude and are out of phase by exactly 90° or one-quarter wavelength.
1) Right-hand Circular Polarization-
- In this form of polarization, the vector rotates in a right-handed fashion.
2) Left-hand Circular Polarization-
- In this form of polarization, the vector rotates in a left-handed fashion, i.e. opposite to right-handed.
3. Elliptical Polarization
- When two linearly polarized waves of unequal amplitudes that are mutually perpendicular to each other are combined then the elliptically polarized wave is produced.
Co-Polarization and Cross-Polarization:
- Co-polar means when the polarization of both the transmitting (test antenna) and receiving antenna (reference horn antenna) is the same.
- Cross polarization means when the polarization of both antennas is different.
