An induction motor is an AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor used to produce torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding.
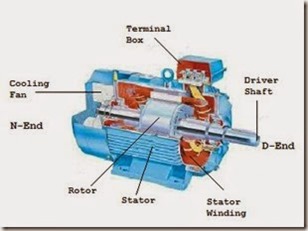
In DC motor, one supply is given to the stator and another to the rotor through brush arrangement. But here in induction motor only the stator winding is fed with an AC supply.
As the supply given to the stator winding, flux will generate in the coil due to the flow of current in the coil. The rotor winding is arranged in such a way that it becomes short circuited in the rotor itself. The flux from the stator cut the coil in the rotor, since the rotor coils are short circuited, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
The current will start flowing in the coil of the rotor. Another flux is generated in the rotor, when current is flowing. Here is two flux stator flux and rotor flux. The rotor flux lags behind the stator flux. Due to this, the rotor will feel a torque, which will make the rotor to rotate in the direction of rotating magnetic flux.
So the speed of the rotor will be depending upon the AC supply and the speed can be controlled by varying the input supply. This is the basic working principle of the induction motor of either type, single phase or 3 phase.
