- An electrical resistor whose resistance varies with the current passing through it, and thus tends to maintain a constant current.
- A device that aids in maintaining the stability of the electrical circuit is a ballast resistor. Utilizing a resistive material that becomes more resistant as the temperature rises produces the ballast effect. These resistors are employed to correct for variations in line voltage as well as other devices’ negative volt-ampere characteristics.

- An electrical component called a ballast resistor regulates the amount of current that flows through a circuit.
- Even when the applied voltage varies, it maintains a constant current flow throughout the circuit. As opposed to load resistors, which have a constant resistance, this resistor acts as the system’s changing load.
Types of Ballast Resistor
There are two types of Ballast Resistor
- Fixed Ballast Resistor
- Self-Variable Ballast Resistor
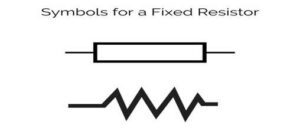
What Is A Fixed Resistor?
- This category includes ballast resistor with a set resistance. It is preferable to have a high resistance value for a variety of applications.
- This kind of ballast resistor is frequently used in straightforward circuits with modest power requirements, like neon or LED lamps. The ventilation fan speed can also be managed by this fixed resistor. The ballast resistor is fixed-resistance and has two center taps.
- Bypassing some of the ballast, the fan speed selection switch selects the entire ballast resistor’s speed with no low-speed option.
- Two terminals simply refer to the two branches or legs of a fixed resistor. A load and a voltage source are linked in series with fixed resistors.
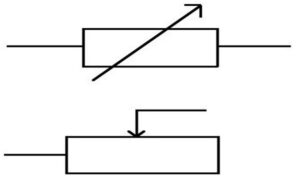
What Is A Self-Variable Ballast Resistor?
- In reaction to changes in current, these ballast resistors can change their resistance. For instance, a rise in current will cause resistance to rising, whereas a fall in current will cause resistance to fall.
- Incandescent light fixtures frequently employ these ballast resistors. The ballast resistor warms up as the current through the lamp increases, and as the temperature rises, so does the resistance, raising the voltage drop across the resistor.
- When the current is reduced, the temperature of the ballast resistor decreases along with its resistance, which causes the voltage to fall.
- In comparison to an appropriate fixed resistor, this kind of ballast resistor has the advantage of allowing for more exact current regulation.
- Another advantage is that the resistive ballast minimizes power loss compared to a fixed resistor because it only loses a tiny portion of total power.
Working Of Ballast Resistor
- The way the ballast resistor works causes the temperature to rise as the current through it rises. The resistance will increase as a result of the temperature increase.
- Therefore, as resistance rises, current passage through the network will be hindered. To start the engine, these resistors are utilized in automobiles. After the motor starter starts the car’s engine, the resistor reduces battery voltage loss.
- Applied lighting technologies like LEDs, neon lights, fluorescent lamps, and others may also make use of it.
- The definition of “ballast” in the English lexicon is something that provides stability. As a result, when we talk about an electrical ballast, we’re talking about a gadget that’s crucial to keeping the electrical circuit stable.
- You might be wondering, though, how it achieves stability. Depending on the circuit in which they are utilized, different electric ballasts limit voltage while others limit current.
- By doing this, they lessen the possibility of an overvoltage or overcurrent in the circuit, improving system stability.
- The complexity of electric ballast varies tremendously. It could be as straightforward as a resistor, capacitor, or inductor, or it could be as complicated as the electronic ballast used in fluorescent lamps.
Advantages Of Ballast Resistor
- These resistors aid in electrical system voltage and current management.
- The equipment is protected from overvoltage and overcurrent by this resistor.
- These resistors reduce current and voltage changes in the remaining parts of an electric circuit.
- As a result, a ballast resistor is typically used in various automotive and lighting circuits for over-voltage, current, or protection to provide circuit stability.
Applications Of Ballast Resistor
- The bulk of these resistor is used in automotive and lighting systems.
- These resistor help prevent overloads and battery drain by regulating the flow of power in an electrical system.
- By interconnecting it in series through the primary winding, this resistor is utilized in a battery ignition system to modify the main current.
- These are employed in vapor lamp and laser circuits to account for variations in line voltage.
- These resistors are used in LED circuits, fluorescent lighting, and automotive applications.
- The ballast in the HeNe laser controls and limits the tube current. Thus, the normal ballast resistance for the majority of HeNe lasers is in the range of 75 K.
- These are present in low-power gadgets like neon and LEDs.
