overview, information, or tutorial about DSSS, direct sequence spread spectrum, and the way that the system operates.
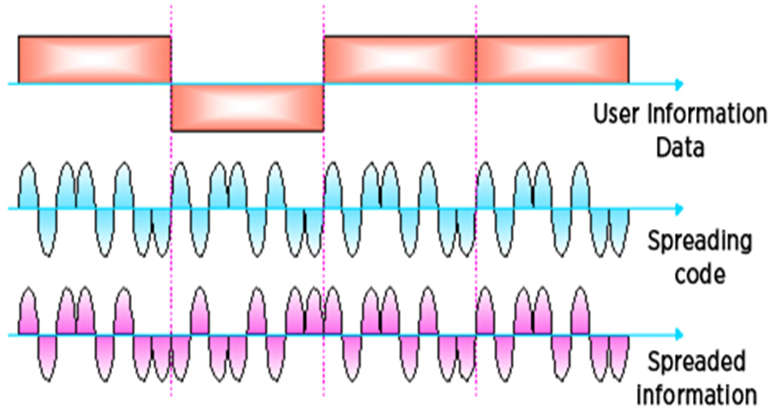
- It is a transmission technology used in local area wireless network transmissions.
- In DSSS technology, a data signal at the transmitter side is combined with a high data rate bit sequence, which divides user data based on a spreading ratio.
- This term is also known as direct sequence code division multiple access.
- DSSS is a technique used for digital signal transmission over airwaves.
- The DSSS is originally developed for military use, and employed difficult-to-detect wideband signals to resist jamming attempts.
- DSSS is also being developed for commercial purposes in local and wireless networks.
- DSSS divided the stream of information into small pieces, each associated with a frequency channel across spectrums.
- In DSSS the chipping code is a redundant bit pattern associated with each bit transmitted.
- It helps to increase the signal’s resistance to interference.
- The original data can be recovered due to the redundancy of transmission if any bits are damaged during transmission.
- This process is performed by multiplying a radio frequency carrier and a pseudo-noise (PN) digital signal.
- The Pseudo-noise code is modulated onto an information signal using several modulation techniques such as quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK), binary phase-shift keying (BPSK), etc.
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Spreading Gain
- The spread spectrum signal will have a significantly broader bandwidth than the initial data stream.
- The spreading gain, a word used to describe the increase in bandwidth, is employed.
- The DSSS spreading gain can be defined as follows if the direct sequence spread spectrum signal’s bandwidth is W and the input data bit length or period 1/R.
Spreading gain =W/R
- It has been discovered that the system performs better the larger the spreading gain of the direct sequence spread spectrum signal.
- This happens as the wanted signal gets stronger.
- The spreading gain in the aforementioned example is four, as can be observed by the fact that four “1”s are produced for each necessary data bit.
- Other dispreading codes would produce data that would appear as noise and be less valuable, so it might be ignored.
Benefits of Using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Resistance to unintended or intended jamming.
- Sharing of a single channel among multiple users.
- Reduced signal/background-noise level hampers interception.
- Determination of relative timing between transmitter and receiver.
Applications of Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- DSSS is used in several GNSS systems like GPS, Galileo, and GLONASS. Cordless phones use DSSS operating in the 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, and 5.8 GHz bands. 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11) and Zigbee, Wireless HART (IEEE 802.15.4) protocols use DSSS. It is also used in automatic meter reading and radio-controlled model automotive, aeronautical & marine vehicle applications.
