What is a Satellite Solar Outage or Sun Outage?
- Sun outage (also known as sun interference or sun fade) is caused by the sun and occurs when the receiving earth station, satellite, and sun are all aligned. This is referred to as the conjunction of the sun and the satellite.
- When the Sun is directly behind a satellite from which an Earth station is attempting to receive or transmit data It usually happens twice a year, and earth stations install temporary or permanent guards to their receiving systems to prevent equipment damage.
Satellite Solar Outage Fundamental
- The phenomenon known as the “spacecraft Sun outage” occurs when solar radiation blocks out radio transmissions from a spacecraft. Because the ground station antenna cannot tell the difference between the Sun’s radiation and the signal it wants to send to the spacecraft, interferences like these develop.
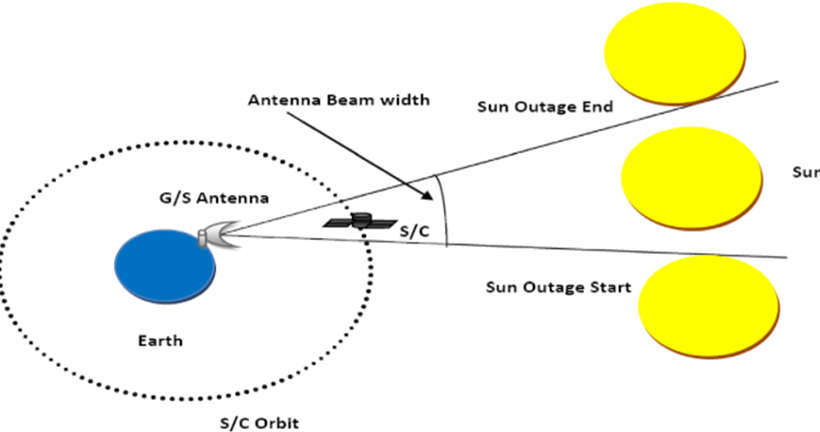
- The solar outage can often impair the received signal for a few minutes every day for a few days for geostationary satellites. Such events’ precise date, time, and length are determined by several variables, including.
- Receiver location.
- The specific satellite’s location.
- Size, or more specifically the antenna’s beam width.
- The Sun’s apparent diameter, as measured from Earth (approximately 0.25°).
- Accuracy of antenna direction alignment concerning the satellite.
- The length of the solar blackout can be greatly affected by factors like antenna directivity. While antennas with higher gain and directivity levels, which are more frequently used for satellite reception, will be affected for considerably shorter periods, those with very wide beam widths could be affected for as long as half an hour. usually just a few moments.
- The outage is caused by solar noise. The effect can produce noise levels between 10 and 20 dB above the signals from transponders, depending on a variety of parameters, even during periods of low solar activity.
Solar Outage Angle
- It is possible to specify the receiving antenna’s so-called blackout angle. The separation angle between the satellite and the Sun (as measured from the ground station antenna) during the beginning or conclusion of a sun blackout or signal degradation is referred to as the solar outage angle of the antenna.
- The length of a solar outage cannot always be predicted with absolute certainty. The actual starting and ending points of the solar outage are progressive transitions. Additionally, there are a lot of variations among various installations and systems. As a result, some stations may have a total signal loss while others may merely see moderate signal degradation.
- As a result, without complete knowledge of the ground station hardware and satellite specifications, it is impossible to precisely determine the solar outage angles. The following equation, however, provides an approximation:Outage angle =
11/(Frequency) x (Diameter) + 0.25°Where (Frequency) = Downlink Frequency in GHz.
Where (Diameter) = Receiver parabolic reflector or dish antenna diameter in meters.
When does the Sun Outage Occur?
- The Southern Hemisphere’s autumnal equinox, as it is known there, occurs in March/April each year. The vernal equinox, which occurs on March 20, is recognized throughout the Northern Hemisphere.
- The sun lines up with your satellite dish and the satellite you are receiving when it crosses the equatorial plane, passing behind geostationary satellites. When the sun passes in front of a satellite, satellite dishes on earth pick up a much stronger signal from the sun, which quickly overwhelms satellite decoders and modems and causes the loss of the satellite signal. The sun is a massive source of broadband electromagnetic radiation, much stronger than the signals broadcast by satellites orbiting the earth.
- Depending on the size of the satellite dish you are using and where you are on the planet, a solar blackout may last up to 10 minutes. The satellite decoder or modem can reacquire the signal from the satellite once the sun has risen from behind it, restoring service.
- After a solar outage, it may occasionally be necessary to restart the satellite decoder or modem to resume service.
- Depending on your position on earth, you can calculate the approximate time a solar outage will affect your ability to receive each satellite. This time will change slightly every day as the equinox approaches and passes.
-
There are numerous calculators available, and it is simple to anticipate the precise dates and times of solar outages. All that is required is knowledge of the satellite’s position (in some cases, just the satellite is required because the calculator may already have its coordinates), as well as the receiver’s location in latitude and longitude.
- It is frequently necessary to know the antenna’s beam width since it will help determine when the satellite solar outage will occur.
Conclusion Of What is a Sun Outage?
- The exact alignment of the sun, satellite, and receiving antenna causes sun outages. It occurs twice a year for a few days and about 12 minutes each time. which causes signal loss in the earthly receiving antennas. It results from thermal noise from the sun interfering with the satellite signal.
- The way these interference works is that, for instance, two people speaking to each other would be P1 and P2, and suddenly P3 would yell at P1. When that happens, P2’s voice will be replaced by P3’s voice alone.
- Sun Outage Occurs two times a year. For Northern Hemisphere, it occurs once in February & March and again in September & October. While for Southern Hemisphere it occurs once in March & April and again in August & September.
