Wave
- Wave refers to a propagating dynamic disturbance that deviates from equilibrium. In many cases, a wave can be described by the wave equation. Physical waves are created by the involvement of at least two quantities in the wave environment.
![]()
- A wave that moves in one direction is called a traveling wave.
- Two waves superimposed in opposite directions form a standing wave.
Wavelength
- Wavelength is referred to the distance between two consecutive peaks or two similar consecutive points in a wave. Wavelength is measured in length units like meters.
Frequency
- In physics, frequency is defined as the number of waves that pass through a point in the unit of time. The frequency of a wave is measured by the unit of Hertz (Hz).
Amplitude
- The maximum amount of displacement of a point of a wave relative to its rest position (equilibrium) is called amplitude. So the amplitude is half of the vibration length. Like wavelength, it is measured in length units.
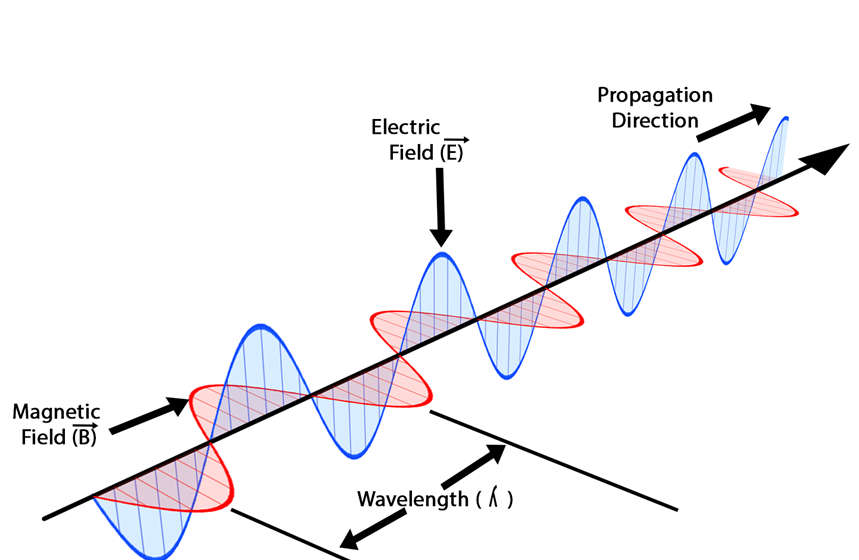
- An Electromagnetic Wave is the result of oscillation between electric and magnetic fields. In other words, it is created by vibrating magnetic and electric fields. It is also called the EM wave.
- Electromagnetic Radiations Electromagnetic radiation generally belongs to those electromagnetic waves that are free from being affected by excitatory charges, in which case they are so-called far fields.
- Near fields are those that refer to currents and their generating charges, such as electromagnetic induction and electrostatic induction.
![]()
