Depletion mode:
When the gate voltage is positive with respect to source, the depletion type MOSFET (metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor) operates in depletion mode.
In the depletion type MOSFET, the device is normally ON at zero gate-source voltage. Such devices are used as load “resistors” in logic circuits. For the N type depletion load devices, the threshold voltage may be about –3 V. It could be turned off by pulling the gate 3 V negative.
Construction:
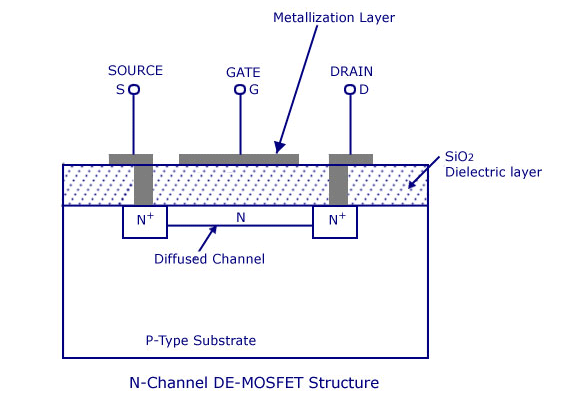
- The construction of depletion type N channel MOSFET (metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor) is shown in above figure.
- It consist conducting bar of N type silicon material with an insulated gate on the left and P region on the right.
- The N channel is formed by distribution between the source and drain. The type of impurity for the channel is the same as for the source and the drain.
- Here is a single P region which is called substrate or body. It physically reduces the conducting path to the narrow channel.
- A thin layer of silicon dioxide is deposited on the left side of the N type channel. This layer insulates the gate from the channel. It has no PN junction.
