- Ground waves are radio waves propagating parallel to and adjacent to the surface of the Earth, following the curvature of the Earth.
- This radiation is known as Norton surface wave, or more properly Norton ground wave because ground waves in radio propagation are not confined to the surface.
- Lower frequency radio waves, below 3 MHz, travel efficiently as ground waves.
- It is known as a ground wave because it is the sum of the waves that are reflected by the earth’s surface or any hills.
- The curvature of the earth is followed by the waves, enabling them to cover beyond the horizon.
- The waves get blocked beyond the horizon, by the curvature of the world and the signals are produced by the diffracted surface wave.
Ground Wave Propagation:
- The process in which radio frequency propagates along the surface of the earth for communication purposes.
- Low frequency of electromagnetic spectrum was used.
- Also called surface wave propagation.
- Collection of this radiation along the earth’s surface is known as ground wave propagation.
- Intensity of radiations drops with distance due to its absorption by ground.
![]()
- Ground propagation works because lower-frequency waves are more strongly diffracted around obstacles due to their long wavelengths, allowing them to follow the Earth’s curvature.
- Ground waves propagate in vertical polarization, with their magnetic field horizontal and electric field (close to) vertical.
- The conductivity of the surface affects the propagation of ground waves, with more conductive surfaces such as seawater providing better propagation.
- Increasing the conductivity of the surface results in less dissipation.
![]()
- Ground wave Propagation is a method of radio frequency propagation that uses the area between the surface of the earth and the ionosphere for transmission.
- The Ground wave can propagate a considerable distance over the earth’s surface Particularly in the low frequency and medium frequency portion of the radio spectrum.
- Ground wave radio propagation is used to provide relatively local radio communications coverage.
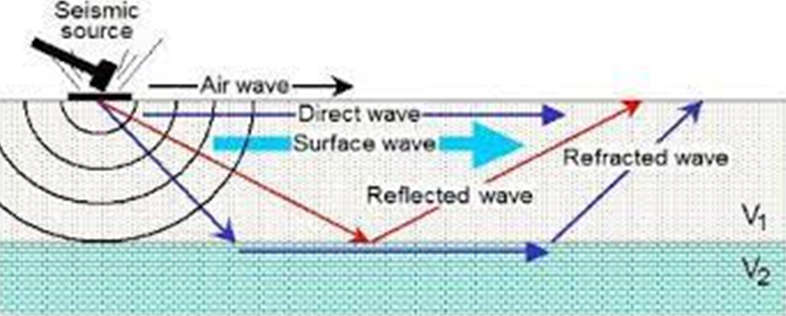
Ground waves are divided into three components:
- Surface Wave
- Direct Wave
- Earth Reflected Wave
- Surface Wave – The component of a ground wave that uses the earth’s surface as the wave conductor
- Direct Wave – The component of a ground wave that propagates through the shortest distance between two points on the earth’s surface.
- Earth-Reflected Wave – The component of a ground wave that gets reflected from the earth’s surface and then travels towards the receiving antenna.
Advantages of Ground Wave Propagation:
- These waves have the tendency to bend around the corners or obstructions during propagation which makes them more efficient and also, these are not affected by the change in atmospheric conditions.
Applications of Ground Wave Propagation:
- These can be used for one-way communication from the military to submerged submarines as they penetrate to a significant depth into seawater.
- AM, FM, and television broadcasting can be done with the help of ground waves.
