What is Thermionic Emission? How Does this process take place?
- The word thermionic is comprised of two words ‘thermal’ which means ‘heat’ and ‘ion’ which is a ‘charge carrier’.
- Thermionic emission is a process in which charged particles (also known as Thermion) are emitted from the heated surface of a metal.
- As the metal is heated the thermal vibrations energy is given to the charged particle which can be an electron or ion and it starts moving away from the center, as soon as the thermal energy increases and overcomes the electrostatic force the thermion is emitted.
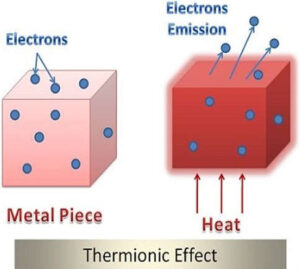
- This process of thermionic emission depends mainly on three parameters, temperature of the metal surface, area of the metal surface, and the work function of the metal. It can be derived from the O. W. Richardson equation as,
J = AT2exp(-W/kT)
- where,
J = current density of the electron emission (mA/mm^2)
A = Plank’s constant in Amperes/m2/k2
T = surface temperature in Kelvin (K)
W = cathode material’s work function in J or eV
K = Boltzmann constant like 1.3806488E^-23 J K-1 - In some electronic devices thermionic emission has an essential role, and the classic example is the of electrons from a hot cathode into a vacuum.
- Another example is the thermionic diode,
![]()
![]()
- A thermionic diode is a vacuum tube diode. The cathode is heated, but the anode is not. When the cathode has negative potential relative to the anode, electrons are charged from the cathode due to thermal vibrations energy(thermionic emission) and travel to the anode through the space. When the voltage reverses, electrons are not able to escape from the cold anode. This makes electron current flow only from cathode to anode, hence the diode characteristic.
Applications of Thermionic Emission
- Thermionic emission is used for various applications such as high-frequency-based vacuum transistors used in electronics, power electronics, electron guns used in scientific instrumentation, x-ray generation & energy converters.
- Anything used for either cooling or generating power utilizes the concept of thermionic emission theory. As temperature increases, the magnitude of the flow increases.<.li>
- It is also used in diode valves, vacuum tubes, cathode ray tubes (CRT), electron microscopes, electron tubes, electrodynamics tethers, etc.
