- The AC circuit is commonly known as an alternating current.
- Impedance is the opposition to the current flowing around the circuit.
- Impedance is a value given in Ohms i.e. the combined effect of the circuit current limiting components within it, such as Resistance (R), Inductance (L), and Capacitance (C).
- In a DC circuit, the opposition to current flow is called Resistance, but in an AC circuit, impedance is the result of both the circuit’s resistive (R) and reactive (X) components.
- In a DC circuit, the amount of electrical resistance present is denoted by the letter “R” and for an alternating AC circuit, the letter “Z” is used to represent the opposition to current flow.
- We observe that impedance (Z) is the combined effect of the total values of the resistance (R) and the reactance (X) present within an AC circuit.
- However, the impedance depends on the frequency and therefore has a phase angle associated with it.
- The reactance phase angle, either inductive or capacitive, is always 90o out-of-phase with the resistive component, so the circuit’s resistive and reactive values cannot be simply added together arithmetically to give the circuit total impedance value. That is R + X does not equal Z.
- The resistance is directly equal to their impedance, (R = Z) because the resistors do not change their value with frequency and therefore have no reactance.
- Therefore the resistors have no phase angle, so the voltage across them and the current flowing through them will always be “in-phase”.
- Although, reactance in the form of inductive reactance, (XL) or capacitive reactance, (XC) does change with frequency, causing a circuit’s impedance value to vary as the supply frequency varies.
Resistance and Inductive Reactance
- The following right-angled graphs show how resistance and reactance are combined with the hypotenuse (longest side) of the triangle representing the complex impedance of the circuit.
![]()
- We can use Pythagoras’s theorem and associated equations to relate the two sides of the right-angled triangle representing resistance and inductive reactance to the length of the third side being the hypotenuse for a three-sided right-angled triangle.
- Pythagoras’s theorem is explained in terms of impedance, resistance, and reactance as being:
Z2 = R2 + X2
That is:
(Impedance)2 = (Resistance)2 + (Reactance)2 - Thus the “Z” is the resulting vector sum of the resistance vector (R) and the reactance vector (XL) and is a positive slope as shown.
Impedance of an RL Circuit
![]()
Phase Angle of an RL Circuit
The angle in degrees between the two vectors is called phase angle (φ).
![]()
Resistance and Capacitive Reactance
- For resistance and capacitive reactance, the right-angled graph uses and combined with the hypotenuse (longest side) of the triangle representing the complex impedance of the circuit.
- Make sure that for a capacitor “Z” is the vector sum of the resistance vector (R) and the reactance vector (XC).
![]()
- Again using Pythagoras’s theorem and equations we can relate the two sides of the right-angled triangle representing resistance and capacitive reactance to the hypotenuse which is the complex impedance.
- In terms of impedance, resistance and reactance the Pythagoras theorem is used.
Impedance of an RC Circuit
![]()
- The angle in degrees between the impedance vector and the resistance vector is called the tangent of the phase angle (φ).
- The phase angle is equal to the reactance divided by the resistance as shown.
Phase Angle of an RC Circuit
![]()
Impedance of an RLC Circuit
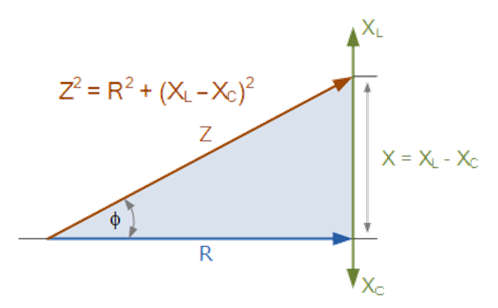
- For resistance and reactance (inductive and capacitive) the vector diagram can be used and combined to form impedance.
- The sum of the inductive reactance, XL, and the capacitive reactance, XC is the combined reactance of the series circuit as shown below.
- X = XL + (-XC) = XL – XC
- Which gives
![]()
