What is Wheatstone Bridge?
- A Wheatstone bridge is a type of electrical circuit that is used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit, one of which contains the unknown component. The circuit’s primary advantage is its ability to provide extremely accurate measurements (in contrast with something like a simple voltage divider). [1] It works in the same way as the original potentiometer.
Construction of Wheatstone Bridge
- The general arrangement of the Wheatstone bridge circuit is shown in the figure below. It is a four arms bridge circuit where arm AB, BC, CD, and AD are consisting of electrical resistances P, Q, S, and R respectively.
- Among these resistances, P and Q are known as fixed electrical resistances and these two arms are referred to as ratio arms. An accurate and sensitive Galvanometer is connected between terminals B and D through a switch S2.
- This Wheatstone bridge’s voltage source is connected to terminals A and C via a switch S1, as shown. Between points C and D, a variable resistor S is connected. By varying the value of the variable resistor, the potential at point D can be changed. Assume currents I1 and I2 flow through the paths ABC and ADC, respectively.
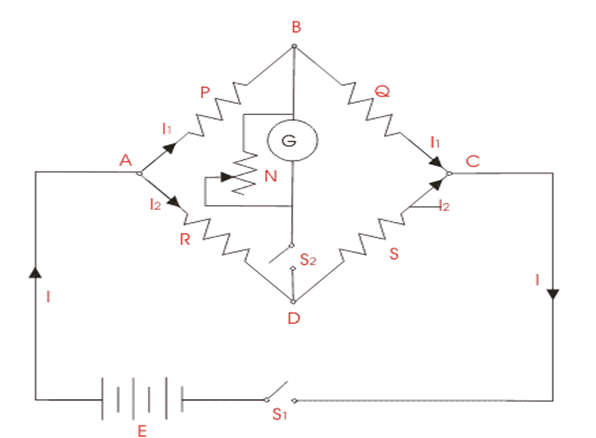
- As long as the voltage across A and C remain constant, changing the electrical resistance value of arms CD will change the value of current I2. If we continue to adjust the variable resistance, a voltage drop across the resistor S, which is I2, may occur. S is exactly equal to the voltage drop across resistor Q, which is I1.Q. As a result, the potential at point B equals the potential at point D, and the potential difference between these two points is zero, implying that the current through the galvanometer is nil. When switch S2 is closed, the deflection in the galvanometer is zero.
Working on the Wheatstone Bridge Circuit
- The Wheatstone Bridge operates on the principle of null deflection or null indication, which means that when the bridge is balanced, the ratio of their resistances is equal and no current flows through the galvanometer.
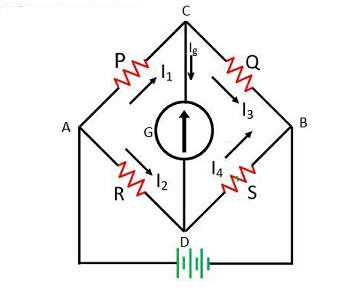
- If the bridge is unbalanced, a potential difference exists between B and D, causing a current to flow through the galvanometer. The known resistance and variable resistance should be varied to achieve a balanced condition. The Wheatstone bridge’s basic circuit is shown below.
let,
P = Resistance of arm AB
Q = Resistance of BC
R = Resistance of AD
S = Resistance of CD
E = Source (battery)
G = Galvanometer (detector). - When the potential difference between points A and B equals the voltage across points A and D, the bridge is said to be balanced (i.e., the potential difference across the galvanometer or BD is zero). As a result, no current flows through the galvanometer, resulting in no deflection (null-deflection).
- The voltage across AB will equal the voltage across AD under balancing conditions, i.e.,I1 P = I2 R.. (I)
- The following conditions exist when the bridge is balanced:
![]()
- Where E is the source’s emf. We get this by substituting the values of I1 and I2 in equation I:
![]()
- Where,R = Unknown resistance
S = Standard arm resistance
P, Q = Ratio arms. - The equation of the Wheatstone bridge under balanced conditions is given above. As a result, if the resistances in the other three arms, P, Q, and S, are known, the value of the unknown resistance R can be calculated using the above equation.
Unbalanced Wheatstone Bridge
- If VOUT in the preceding circuit is greater than zero (VOUT 0), the Wheatstone is said to be an Unbalanced Wheatstone Bridge. The Unbalanced Wheatstone Bridge is commonly used for measuring various physical quantities such as pressure, temperature, strain, and so on.
- For this to work, the transducer must be of the resistive type, which means that its resistance changes when the quantity being measured (temperature, strain, etc.) changes.
Limitations of Wheatstone Bridge
- If the Wheatstone bridge is unbalanced, it gives inaccurate readings.
- It is an extremely sensitive device.
- It measures resistances ranging from a few ohms to several kilo-ohms.
Applications of Wheatstone Bridge
- The Wheatstone bridge is used to measure low resistance precisely.
- Temperature, light, and strain are all measured using a Wheatstone bridge and an operational amplifier.
- Variations on the Wheatstone bridge can be used to measure impedance, inductance, and capacitance.
